
Fix Buffering Problems on Rural and RV 5G Internet
Posted by James on
That dreaded spinning wheel is infuriating, especially when you’ve put your money and trust into a 5G setup for your rural home or RV. When your stream grinds to a halt, it's usually down to one of three culprits: network congestion, a weak signal from a distant cell tower, or physical objects messing with the connection. Getting it fixed means tackling both your physical setup and how you manage your data.
Why Your 5G Internet Keeps Buffering

It’s a story I hear all the time. You were sold on the promise of lightning-fast 5G, but your evening movie night is more buffering than binging. This isn't just "slow internet"—it's a more complicated issue, especially for those of us trying to stay connected in remote or mobile settings.
Once you understand what’s really going on behind the scenes, you can start to find a real, lasting solution. The problem usually boils down to a few key issues that are magnified when you aren't plugged into a traditional cable or fiber line.
Common Causes of Buffering on 5G
For those of us in the country or on the road, the buffering battle is often fought on three fronts:
- Network Congestion: Your 5G connection is a shared highway. During peak hours—think evenings and weekends—everyone in your area jumps online to stream, game, and browse. The local cell tower gets swamped with traffic, and there’s just less bandwidth to go around for you. The result? That frustrating spinning circle.
- Signal Strength and Quality: This is a big one. The physical distance between your router and the nearest cell tower is absolutely critical. A weak signal has to fight to deliver data, making your connection fragile and prone to interruptions. It's like trying to have a conversation from across a crowded, noisy room.
- Physical Obstructions: That 5G signal has to travel through everything between the tower and your router—walls, trees, hills, and other buildings. The very materials of your home or RV, like metal siding, tinted windows, and even dense trees, can drastically weaken or block the signal before it even gets inside.
This isn't just a local headache; it's a reflection of a massive global trend. Buffering has become a major challenge as video streaming now dominates how we use the internet. Worldwide, mobile users chew through over 147 billion gigabytes of data every month, and video is responsible for a staggering 110 billion of those gigabytes. With that kind of demand, even a small hiccup in the network can bring your stream to a screeching halt.
To get a handle on what's causing your specific buffering woes, it helps to see the common culprits laid out.
Common Buffering Causes and Quick Fixes
I've put together a quick table to summarize the most frequent issues I see with rural and RV 5G internet. Think of this as your first diagnostic checklist.
| Problem Area | What It Means for You | First Step to Fix |
|---|---|---|
| Network Congestion | Your internet slows to a crawl during peak hours (evenings, weekends) because the local tower is overloaded with users. | Try streaming or downloading large files during off-peak hours, like late at night or early in the morning. |
| Weak Signal | You're far from the nearest cell tower, resulting in a weak, unstable connection that drops frequently. | Move your router to a window or higher floor on the side of your house facing the likely direction of the tower. |
| Physical Obstructions | Walls (especially metal in RVs), trees, or hills are blocking the 5G signal from reaching your router effectively. | Identify and minimize obstructions. An external antenna is often the best long-term solution to bypass these barriers. |
| Too Many Devices | Multiple phones, TVs, and computers are all trying to use the same limited bandwidth at once, overwhelming your router. | Disconnect devices that aren't actively being used. Prioritize the device you're using for streaming. |
This table should give you a starting point. By identifying the most likely cause, you can take the right first step toward a smoother, buffer-free connection.
Key Takeaway: Buffering on your 5G isn't a sign of "bad" service. It's about overcoming the unique challenges of a wireless, shared network. You have to account for congestion, distance, and physical barriers that get in the way of a smooth data flow. Understanding these factors is the first and most important step, especially as you explore options for reliable rural high-speed internet that can truly close the connectivity gap.
Find the Strongest 5G Signal in Your Space
If you want to put an end to buffering for good, you have to go straight to the source: the 5G signal itself. Sure, plopping your router by a window is a start, but it’s really just a shot in the dark. A much smarter approach is to methodically map out the signal “sweet spots” in your RV or home.
Believe me, this isn’t nearly as technical as it sounds. My go-to method is dirt simple. I just grab a roll of painter's tape and my 5G router, and I start testing. I’ll move the router to a bunch of different spots—high up on a cabinet, down low, near every single window, and on all sides of the RV. At each location, I put a small piece of tape to mark the spot. This gives me a repeatable grid for my tests.
With my test grid laid out, I check the router's signal metrics at each piece of tape to see which spot gives me the best numbers. This little bit of effort takes all the guesswork out of the equation.
The Signal Metrics That Actually Matter
To hunt for that perfect signal, you need to know what you’re looking for. Forget about the simple "bars" on your phone; we need to look at the real data inside your router's admin panel or app. Two numbers tell the true story of your connection quality.
-
RSRP (Reference Signal Received Power): This is all about signal strength. Think of it as how loudly the cell tower is "shouting" at your router. You're looking for a number closer to -80dBm. A number like -110dBm is a much weaker, quieter signal.
-
SINR (Signal to Interference plus Noise Ratio): This is signal quality. It’s about clarity—how much of the signal is useful versus how much is just background noise and interference. You want a high positive number, like 20dB, which is fantastic. A low or negative number means you’ve got a noisy, choppy connection that’s prone to dropouts.
The single most important thing you can do to fix buffering—before you even think about buying new antennas or boosters—is to find the spot with the best combination of RSRP and SINR. You can have a powerful signal, but if it's in a bad location, it's still a bad signal.
Don’t underestimate how much your rig’s construction affects this. An RV with aluminum siding is like a fortress against cell signals, while one with fiberglass walls is much more forgiving. In a house, brick and concrete are notorious signal killers. This is why testing multiple locations, especially windows facing different directions, is so critical to getting a stable connection.
Of course, your experience depends heavily on where you are. As of early 2025, there are over 5.56 billion internet users worldwide, but the quality of their connection is wildly different. While nearly 99% of people in Northern Europe have solid internet, folks in other regions struggle with buffering because the infrastructure just isn't there. You can read more about global internet access disparities to see how this impacts user experience.
Even your own setup can be the weak link. Running a long, cheap cable from an external antenna to your router can kill a great signal before it ever gets to your devices. Always, always use the shortest, highest-quality cable you can to hold onto every bit of performance you've worked so hard to find.
Choosing Hardware That Ends Buffering for Good
So, you’ve tried moving your router around, fiddling with the settings, and you’re still getting that dreaded buffering wheel. I’ve been there. When basic tweaks don’t cut it, it's time to look at the gear itself. To truly solve buffering issues, especially if you’re in a rural home or an RV, investing in the right hardware is the final, most impactful step you can take.
That little mobile hotspot your carrier gave you? It’s a decent starting point, but it was never really designed to handle a whole family streaming, gaming, and video conferencing at once—especially not in a weak signal area. Upgrading to a dedicated cellular router is a game-changer. These are built for the heavy lifting, with powerful processors to manage a ton of traffic and much better Wi-Fi to blanket your entire space, killing those frustrating dead zones.
This image gives you a good idea of where a solid 5G cellular setup fits in with other internet options.
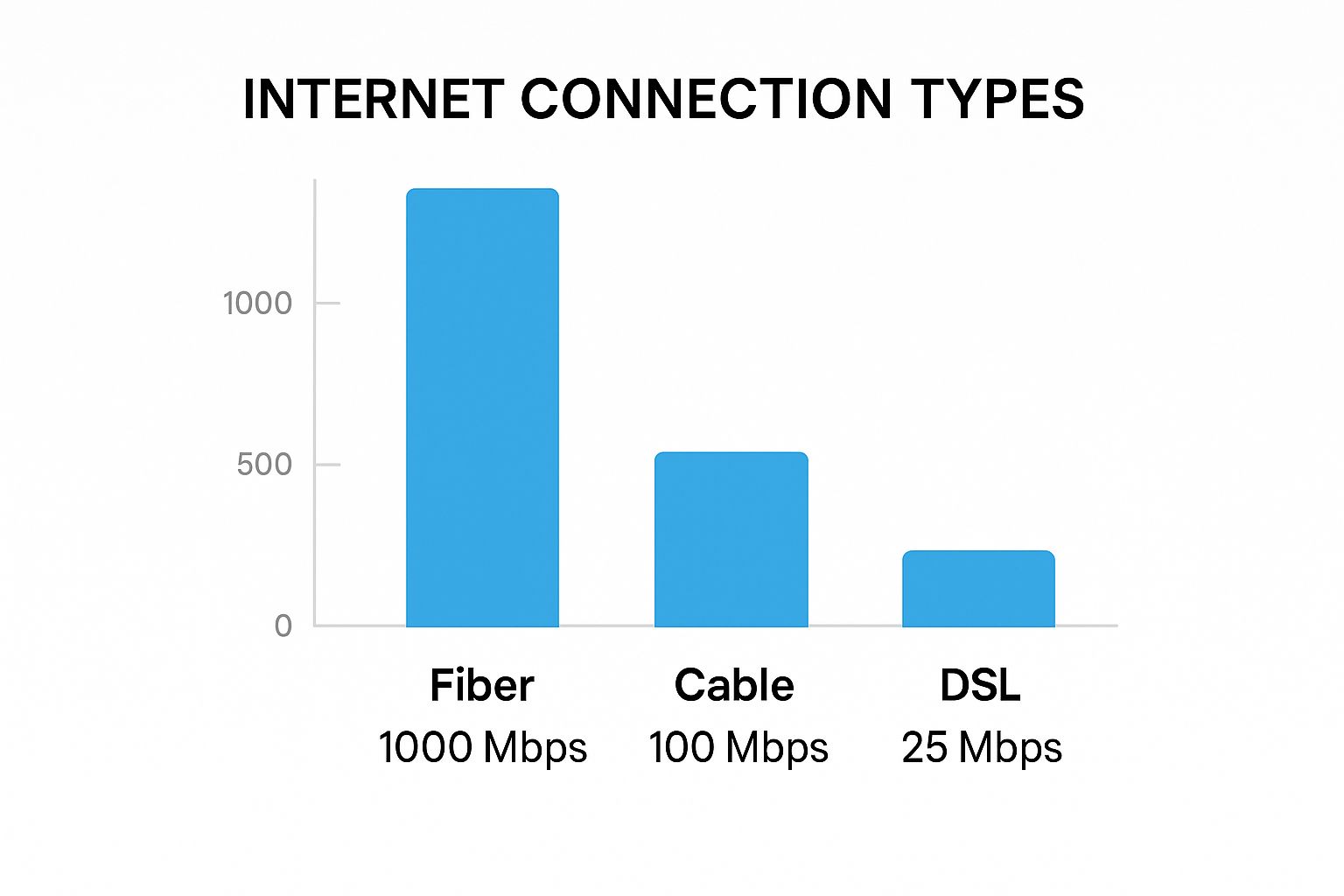 Sure, fiber is the gold standard for speed, but it’s a pipe dream for most of us in rural or mobile situations. That makes a high-performance 5G setup the most realistic and powerful choice available.
Sure, fiber is the gold standard for speed, but it’s a pipe dream for most of us in rural or mobile situations. That makes a high-performance 5G setup the most realistic and powerful choice available.
The Power of an External Antenna
If there’s one piece of hardware that will make the biggest difference, it’s an external antenna. Think of it like a powerful hearing aid for your router. By mounting it outside, you get it away from all the stuff that blocks cell signals—like your RV’s metal skin or the thick walls of your house. It captures a much cleaner, stronger signal from the cell tower than your router ever could on its own.
There are two main flavors of antennas, and picking the right one depends entirely on your situation.
- Omni-Directional Antennas: These are the perfect companion for anyone on the move. They pull in signal from every direction (a full 360 degrees), which means you don’t have to mess with aiming it every time you pull into a new campground. Set it and forget it. They’re built for convenience and reliable performance for the constant traveler.
- Directional (Yagi) Antennas: Now, these are for stationary folks in a rural home or a long-term RV spot. A directional antenna focuses all its energy in one direction, like a laser beam. This allows you to lock onto a single, far-off cell tower with incredible precision, pulling in a stable, fast signal that you might have thought was impossible to get.
To help you decide, here’s a quick breakdown of how they stack up.
External Antenna Comparison for RV and Rural Homes
| Antenna Type | Best For | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Omni-Directional | RVers, boaters, and anyone frequently changing locations. | Easy setup, no aiming required, good for picking up signals from multiple nearby towers. | Less powerful for very long-distance signals. |
| Directional (Yagi) | Stationary rural homes, long-term RV sites, workshops. | Excellent for pulling in weak, distant signals. Can significantly boost speed and stability. | Requires careful aiming at a specific cell tower; needs to be re-aimed if you move. |
Choosing the right antenna is about matching the tool to the job. For life on the road, an omni-directional is your best bet. For a fixed location, a directional antenna will give you the absolute best performance.
For a deeper look at different setups and how to install them, our guide on how to get internet in an RV has some great, easy-to-follow solutions.
Why a Cellular Router Beats a Hotspot
A dedicated cellular router is the command center of your network, and it’s leagues ahead of a simple hotspot. These routers are engineered to juggle multiple devices at once without breaking a sweat. Someone can be streaming a 4K movie while another person is on a crucial video call, and the connection stays solid. They also unlock advanced features like band-locking, which lets you force the router onto a specific, less-crowded 5G frequency for even better performance.
Key Insight: The ultimate fix for a stationary rural home is combining a directional antenna with a high-quality cellular router. This setup directly attacks the two main causes of buffering: a weak signal and hardware that can't keep up.
This combination creates an incredibly robust system that feels just like reliable home internet. It's interesting to see how similar principles are being applied elsewhere; for instance, understanding how Technology Is Changing The Hotel Room shows how important robust hardware and network infrastructure are becoming everywhere, which can inspire how you optimize your own connection.
Fine-Tune Your Network and Device Settings

Before you even think about spending another dollar on new gear, you should know that some of the most effective ways to fix buffering problems are completely free. They're right there at your fingertips, hiding in your device and network settings. Taking control of these settings puts you in the driver's seat of your own bandwidth.
Let's start with an easy one: managing your streaming quality. Manually telling services like Netflix or YouTube to stream at 1080p instead of 4K can make a world of difference. On the smaller screens typical in an RV or on a laptop, you'll barely notice the visual change, but you'll absolutely feel the improvement in stability.
This one simple tweak drastically cuts down on how much data you're pulling, easing the strain on your connection and making that dreaded buffering wheel far less likely to appear.
Tame Your Background Data Hogs
One of the sneakiest culprits of unexpected buffering is all the data your devices gobble up in the background. Your gadgets are constantly syncing files, downloading app updates, and who knows what else, all while competing for a slice of your internet pie. This is where a little strategic scheduling becomes your secret weapon.
Think about those massive video game updates or big operating system patches. They're total bandwidth vampires. Instead of letting them download right in the middle of movie night, jump into your device settings. Configure them to handle these huge downloads during off-peak hours, like between 2 a.m. and 5 a.m., when the network is asleep.
Key Takeaway: You are the traffic controller for your own network. By pushing high-bandwidth activities to the middle of the night and dialing back your stream quality, you free up the pipeline for a smooth, buffer-free show when you actually want it.
It's a lot like how businesses look for strategies to improve operational efficiency in their daily work. You're just applying the same smart thinking to make sure your connection and devices are working together, not against each other.
Keep an Eye on Hidden Network Traffic
It’s not just the obvious downloads you need to watch out for. The web has gotten more complex, and there are new, often invisible, layers of data usage that can absolutely lead to buffering.
AI-driven content delivery and ad analytics, for example, create a surprising amount of data churn on your network without you even realizing it. All this extra chatter adds to the overall load and can push your connection over the edge. If you want to dig deeper into these kinds of issues, our guide on slow internet troubleshooting has more detailed steps.
This isn't just a hunch; it's a growing trend. Being mindful of these hidden data hogs and managing them through your settings is a critical step in reclaiming your bandwidth for what you actually want to do.
Advanced Strategies for Uninterrupted Streaming
When you’ve tried all the basic fixes but still see that dreaded buffering wheel, it’s time to pull out the heavy hitters. These are the power-user tools that put you in complete command of your connection. Think of this as moving beyond simple tweaks and taking direct control of your network traffic.
This is where we get serious about creating a rock-solid connection, especially for those of us who depend on the internet for work or simply can't stand having our movie night interrupted.
Combine Internet Sources with Load Balancing
Honestly, one of the most bulletproof ways to fix buffering problems for good is to stop relying on a single internet source. By using two connections at the same time—a technique called load balancing or connection bonding—you create a powerful safety net. This approach is an absolute game-changer for RV and rural folks who need maximum reliability.
Let's say you have both a 5G home internet plan and a Starlink dish. A router built for load balancing can intelligently split your internet usage between both of them. If your 5G signal suddenly drops because the local tower gets congested, the router instantly and automatically shifts the heavy lifting over to Starlink. Your Netflix stream won't even hiccup.
I've seen this setup save the day time and time again. It’s so effective because:
- You have a backup: If one service completely dies, the other is already running and takes over in a heartbeat.
- You get more bandwidth: With two pipes feeding your network, you can support more devices and more demanding tasks simultaneously.
- Your connection is smoother: It evens out the natural ups and downs you get with a single, sometimes flaky, connection.
Yes, this means a more advanced router and paying for two internet plans. But for anyone who can't afford downtime, the peace of mind is worth every penny.
By combining two different types of internet, like cellular and satellite, you're not just getting more speed—you're getting a fundamentally more resilient connection that can withstand the unique challenges of remote locations.
Master Your Router’s Quality of Service Settings
Even if you’re sticking with just one internet source, you can still play traffic cop. Most modern routers have a feature called Quality of Service (QoS), which is basically a VIP lane for your most important data. When you set it up right, QoS makes sure your video stream gets the bandwidth it needs, even when other devices on your network get greedy.
For example, you can go into your router’s settings and tell it to prioritize all data flowing to your smart TV or streaming box. If someone else on your Wi-Fi then decides to download a massive video game, the router will protect the bandwidth going to your TV first. That huge download won't get to bully your movie into a buffering spiral.
Here’s how that plays out in the real world:
| Scenario Without QoS | Scenario With QoS |
|---|---|
| A huge game download starts, stealing bandwidth from your movie and causing it to buffer endlessly. | The game download is automatically put in the slow lane, letting your movie stream smoothly without a single interruption. |
| A work video call becomes choppy and pixelated because someone’s laptop is syncing files to the cloud. | The video call is given top priority, guaranteeing it gets a stable flow of data for crystal-clear audio and video. |
Diving into your router’s admin panel to tweak QoS settings can feel a bit technical at first, but it’s one of the most powerful free tools you have. You’re literally telling your hardware what matters most to you. It's a direct and incredibly effective way to fix buffering problems at the source.
Of course. Here is the rewritten section, crafted to sound like an experienced human expert and match the provided examples.
Your Top 5G Buffering Questions, Answered
Over the years, I've heard just about every question you can imagine when it comes to getting a stable 5G connection in an RV or out in the country. Let's tackle some of the most common ones I get. These are the tricky, "but what about..." scenarios that often stand between you and a smooth stream.
Can a VPN Really Cause My 5G to Buffer?
Yes, it absolutely can. A VPN is a fantastic tool for privacy, but it works by adding an extra step to your internet connection. It has to encrypt your data and route it through a separate server, which naturally creates a bit of overhead and can slow things down. If your stream starts lagging the second you connect your VPN, you've likely found your culprit.
A quick way to confirm this is to turn the VPN off and run a speed test. See a big jump in speed? The VPN is definitely part of the problem. Don't worry, you don't have to give it up. Try connecting to a VPN server that's physically closer to you—this shortens the distance your data has to travel. I'd also recommend investing in a premium VPN service; they often use much faster, modern protocols specifically designed to handle high-bandwidth activities like streaming with minimal speed loss.
Will a Different 5G Data Plan Actually Help Fix Buffering?
It definitely can, especially if you’re running into the invisible walls of data caps or network deprioritization. This trips up a lot of people. Many so-called "unlimited" 5G plans aren't truly unlimited at all. They come with a fine-print threshold, often around 50GB or 100GB of what they call "premium data."
Once you burn through that premium data, your provider is free to slam on the brakes, throttling your speed way down. This slowdown is most noticeable during the evening when everyone else is online. It’s the classic story: your internet is blazing fast for the first two weeks of the month, then suddenly slows to a crawl.
Dig into the fine print of your plan and look for terms like "premium data" or "deprioritization." Upgrading to a plan with a higher data cap—or even a true business-level plan that isn't subject to these slowdowns—can make a night-and-day difference for consistent, buffer-free streaming.
Why Does My Internet Buffer at Night but Work Fine in the Morning?
This is the textbook symptom of network congestion. Think of your local cell tower like a highway. During the day, traffic is light. But come evening, it's rush hour. Everyone in your area gets home, and they all jump online at once—streaming movies, gaming, and scrolling through social media.
This flood of activity puts a massive strain on the tower's available bandwidth. Because 5G is a shared resource, your personal slice of the pie gets smaller when the network is overloaded. To fight back against these peak-hour slowdowns, I often recommend using a directional antenna to lock onto a less-crowded tower. You can also dive into your router's settings and configure Quality of Service (QoS) to tell it your streaming device should always get priority.
For Streaming, Should I Use 5GHz or 2.4GHz Wi-Fi?
For streaming, the 5GHz Wi-Fi band is almost always the winner, but there’s a big "if"—if your device is close to the router. The 5GHz band offers much faster speeds and is less prone to interference from other gadgets like microwaves and cordless phones. It's the clean, open freeway of Wi-Fi.
The trade-off? Range. 5GHz signals just don't have the muscle to punch through walls and floors like the older 2.4GHz band does. So, if your smart TV is three rooms away from your router, you're better off with a stable connection on the slower 2.4GHz band than a weak, stuttering signal on 5GHz.
My rule of thumb is pretty simple:
- Use 5GHz for any device in the same room as your router.
- Stick with 2.4GHz for anything farther away that needs a more reliable connection.
For a connection that’s built to conquer the challenges of rural and RV living, SwiftNet Wifi provides high-speed 5G internet designed for reliability where you need it most. Explore our plans and hardware at https://swiftnetwifi.com.


















































