
A Guide to Rural 5G Coverage for Homes and RVs
Posted by James K on
If you've ever watched a video call freeze mid-sentence or a file upload crawl to a halt in a remote location, you know the frustration of bad internet. Let's be honest: true rural 5G coverage is still very much a work in progress, with huge gaps once you get outside of major cities. Good, dependable solutions are out there, but they almost always require specialized gear and providers who know what they're doing.
Understanding the Rural 5G Coverage Gap
Think of the nationwide 5G network as a massive new highway system that's still being built. The superhighways linking big cities are paved, fast, and smooth. But the smaller country roads—the ones leading to scenic overlooks, small towns, and rural homes—are often still gravel, or haven't even been started yet. This is the perfect picture of rural 5G coverage today. The potential is incredible, but the actual infrastructure just isn't there for most people.
For RVers, remote workers, and anyone living outside a major metro area, this "digital divide" isn't a talking point; it's a daily reality. The promise of lightning-fast speeds often crashes into the real-world experience of dropped calls and endlessly buffering videos.

Why Progress Feels So Slow
The slow rollout isn't because the carriers aren't trying; it's a matter of simple physics and economics. Building out this kind of infrastructure is a monumental undertaking, and rural areas present some tough challenges:
- Geographic Barriers: Trees, mountains, and even rolling hills can easily block the high-frequency signals that make 5G so powerful.
- Infrastructure Costs: Laying fiber optic cables and putting up new cell towers in sparsely populated areas just doesn't offer a great return on investment for the big carriers.
- Population Density: Naturally, carriers are going to upgrade their networks where the most customers are packed together—in cities and their suburbs.
This urban-first focus creates a significant lag for the countryside. Progress is happening, but it’s gradual. Data from Q2 2023 showed rural 5G availability hitting 24.8%, an increase from 20.7% the year before. While that’s movement in the right direction, it still leaves the vast majority of rural America waiting. This slow-but-steady pace is exactly why specialized internet solutions are so critical right now. You can see a more detailed breakdown in this analysis of 5G accessibility data.
The reality is that major telecom companies have historically overlooked rural communities. Their business models are built around population density, leaving millions of people with subpar internet options.
Bridging the Digital Divide
This is precisely where specialized providers come into the picture. Companies that focus only on rural and mobile connectivity are stepping in to fill the gaps the big guys leave behind. By using more powerful hardware and finely-tuned data plans, they can grab and amplify existing cell signals to deliver a stable, high-speed connection where you thought it was impossible.
For RV owners and people with homes out in the country, this means you don't have to wait for the national networks to finish paving every last back road. The right equipment and the right service can get you the reliable internet you need today, whether you're parked by a mountain lake or working from your rural homestead. Our guide on securing internet access for rural areas dives deeper into how you can overcome these challenges.
How to Read 5G Coverage Maps and Find a Signal
Before you drop a dime on any new hardware or data plans, your first job is to become a bit of a signal detective. Nailing down reliable rural 5G coverage means looking past the flashy marketing claims and learning to read the coverage maps for what they really are. Carrier maps are a decent place to start, but they’re almost always optimistic, painting huge swaths of color over areas where the signal might be spotty at best—or completely absent.
Think of a carrier’s official map like a weather forecast. It gives you the general picture, but local conditions can be wildly different on the ground. A colored-in patch of "5G coverage" doesn't guarantee a solid signal inside your house or at that perfect campsite you found. Hills, thick woods, and even the materials your RV is made of can block or weaken the signal, a reality these maps just can't show.

Decoding the Different Flavors of 5G
When you pull up these maps, you’re often hit with a confusing mess of terms. It's really important to know what they mean for your actual internet experience, because—and this is key—not all 5G is the same.
- 5G (Nationwide/Low-Band): This is the most common flavor of 5G you'll find, often built on the same towers as the existing 4G LTE network. It has the best range, which is why it’s the most likely type of rural 5G coverage you'll encounter. Speeds are a step up from 4G, but the real win is a more stable, consistent connection.
- 5G+ / 5G UW (Ultra Wideband) / 5G UC (Ultra Capacity): These are just the carriers' brand names for their super-fast, high-speed networks (mid-band and high-band mmWave). They deliver mind-blowing speeds but come with a major catch: the signal travels a much shorter distance and gets blocked easily by obstacles. You’ll almost never find this kind of 5G out in the countryside.
So, when you're checking maps for a rural home or an RV park, you are pretty much always looking for that standard, low-band 5G signal. If the map only shows the ultra-fast stuff, chances are you won't get a usable connection without some serious gear.
Moving Beyond Carrier Maps with Real-World Data
While the carrier maps are a necessary first step, you absolutely have to back up their claims with real-world, user-submitted data. This is where third-party tools become your best friend, giving you a much truer sense of on-the-ground performance. They gather speed test results from thousands of actual users, showing you what kind of speeds people are really getting in a specific spot.
Don't just trust the advertised coverage; verify it. Third-party maps use crowdsourced data from actual users, providing a ground-truth look at signal strength and speed that carrier maps often miss. This is the single most important step in assessing true rural 5G coverage.
Here are the best tools for the job:
- Opensignal: This site offers independent coverage maps and performance stats for all the major carriers. You can compare network availability, download speeds, and even video streaming quality based on data from real people.
- Ookla's Speedtest Map: This global map pulls data from countless speed tests. You can filter by carrier and zoom into your location to see the actual speeds people have clocked in the very areas you plan to live or travel.
By cross-referencing data from tools like these with the carrier's own maps, you can get a much clearer, more confident picture of whether a location has a shot at reliable 5G internet before you commit to anything.
Why Getting 5G in Rural Areas Is So Hard
Have you ever wondered why your phone shows five full bars of 5G in the city, but the signal completely vanishes the moment you hit a country road? It’s not just you. This gap in rural 5G coverage isn't some minor inconvenience; it's the result of some serious technical and financial hurdles carriers have to overcome to push their networks beyond city limits.
At its core, the problem boils down to the physics of radio waves. It helps to think of 5G signals in two different flavors. The super-fast, high-frequency millimeter wave (mmWave) 5G you find in dense urban areas is like a bright, powerful flashlight. It lights up a small area with incredible intensity but doesn't reach very far and gets easily blocked by walls, trees, or even a heavy downpour.
On the other hand, the low-band 5G needed for rural areas is more like a wide-beam floodlight. It can blanket a huge area, traveling for miles from a single tower, but its light just isn't as intense. This means it can provide coverage, but the speeds won't be nearly as mind-blowing as its city cousin.
The Obstacle Course of Rural Deployment
Beyond the signal physics, carriers are up against a tough and expensive landscape when building out rural infrastructure. The path from a cell tower to your device is littered with obstacles that just don’t exist in a flat, predictable city.
Here are the major hurdles they face:
- Challenging Terrain: Mountains, dense forests, and even rolling hills can literally block 5G signals, creating "dead zones" where you have no coverage at all. Unlike cities where signals can bounce off buildings to find a path, natural landscapes tend to just absorb and obstruct them.
- Sky-High Infrastructure Costs: Every single cell tower needs a high-speed backbone to connect it to the internet, which is almost always a fiber optic cable. The cost of digging trenches and laying miles of fiber to a single remote tower can be astronomical, often running into the hundreds of thousands of dollars.
- A Tough Business Case: From a purely financial standpoint, carriers are always going to prioritize areas with the highest population density. One tower in a city can serve thousands of paying customers, but a rural tower might only serve a few dozen. That makes the return on investment (ROI) a much harder pill to swallow.
The economics of rural broadband are just plain difficult. Carriers have to spend more money per person to build the network, only to earn less revenue in return. This financial equation is the single biggest reason the rural coverage gap is still so wide.
A Slow but Steady Expansion
Despite these challenges, things are slowly getting better. Government initiatives and evolving technology are gradually pushing the boundaries of rural 5G coverage. For example, in the U.S., 5G availability in rural spots climbed from 20.7% in mid-2022 to 24.8% by mid-2023.
While that shows progress, it still lags way behind the 35% availability in urban areas, proving a stubborn divide remains. You can see more on this in a deep dive into rural vs urban 5G availability.
This slow, expensive rollout is exactly why you can't always count on the major carriers to deliver a perfect signal straight to your door. It’s also why specialized providers, who use advanced hardware to grab and amplify whatever signal is out there, have become so essential for connecting the countryside.
Your Toolkit for Unlocking Reliable Rural 5G
Alright, we've talked about the challenges of sniffing out a signal. Now let's get our hands dirty and talk about the gear that actually makes rural 5G work. Grabbing a faint, distant signal and transforming it into fast, reliable internet for your home or RV takes the right tools. We're moving beyond your phone's simple hotspot and building a serious system designed for the unique demands of rural 5G coverage.
The brain of this whole operation is a 5G cellular router. Think of it as the command center for your internet. Its one job is to latch onto the best possible cellular signal from the nearest tower, then turn it into a strong, stable Wi-Fi network for your home or rig. Unlike a basic hotspot, a dedicated router is built to run 24/7, handling heavy use from multiple devices without breaking a sweat.
This router becomes the central hub for everything—your computers, smart TVs, phones, you name it. It's the critical bridge between the cell towers out there and all the devices in your digital life.

The Power of External Antennas
If the router is the brain, then an external antenna is its superpower. It's easily the most important piece of your kit.
Imagine a faint radio station crackling in the distance. An external antenna is like a massive signal-boosting dish for your router. It gives it the ability to hear signals that are far too weak to detect on its own, which can make a night-and-day difference in your connection's speed and stability.
An antenna gives your system a huge leg up by getting the reception point outside your home or RV. This lets you completely bypass signal-killing materials like metal siding, insulated walls, and energy-efficient windows that can choke an indoor signal. You'll generally run into two types, and each is designed for a specific job.
An external antenna is the single most effective upgrade you can make to improve your rural 5G coverage. It's the difference between a frustrating, barely-usable connection and a smooth, dependable one.
Omnidirectional vs. Directional Antennas
Picking the right antenna comes down to one thing: how you plan to use your internet. Both are great tools, but they work in completely different ways.
-
Omnidirectional Antennas: These antennas are the "set it and forget it" option. They pull in signals from all directions—a full 360 degrees. This makes them perfect for RVers and anyone on the move. You don't have to aim them. Just mount it, and it will find the best tower wherever you happen to park. Their flexibility is their biggest advantage.
-
Directional Antennas: Just like the name implies, these have to be aimed like a sniper rifle directly at a specific cell tower. They have a much narrower focus but offer way more "gain," meaning they can lock onto a much weaker signal from much farther away. This makes them the ideal choice for a stationary home where you can find the best tower and dial in the strongest possible connection.
Many of the same ideas apply to boosting any cellular signal. For a deeper dive, check out our guide on boosting cell phone signals to learn more.
Mounting and Placement for Maximum Performance
Where you put your antenna matters just as much as which one you buy. The goal is simple: get it as high as possible with the clearest possible view of the cell tower.
Here are a few best practices from the field:
- Go High: Mount the antenna on the roof of your house or RV. Every foot of elevation you gain helps you clear obstacles like trees, hills, and your neighbor's barn that can block or weaken the signal.
- Aim for a Clear View: If you're using a directional antenna, use an app like CellMapper or OpenSignal to pinpoint the exact location of the best tower and aim your antenna right at it. Seriously, even a few degrees of adjustment can make a massive difference.
- Minimize Cable Length: Use the shortest possible run of high-quality coaxial cable to connect the antenna to your router. The longer the cable, the more signal you lose before it even gets to the router.
When you combine a powerful 5G router with the right external antenna, you're building a specialized system that can pull in excellent rural 5G coverage in places most people assume are dead zones. Beyond just the hardware, applying some general reliability principles will also go a long way in keeping your connection solid.
Comparing Your Rural Internet Options
Once you know that rural 5G coverage is a possibility where you are, the next move is to see how it stacks up against the other options out there. 5G isn’t the only game in town, and for anyone living out in the country or on the move in an RV, the main rivals are satellite internet (think Starlink), Fixed Wireless Access (WISP), and good old cellular boosters.
Each one of these has its own personality, with a unique set of pros and cons. The right choice really boils down to what you need. Are you a gamer who can't stand lag? A remote worker who lives on video calls? Or an RVer who needs true, work-from-anywhere portability? Let’s break down how they compare on the things that actually matter.
Rural Internet Technology Showdown
To make this simple, we've put together a straightforward comparison of the most common internet options for rural homes and RVs. This table cuts through the marketing fluff and focuses on the key performance and usability factors you'll experience day-to-day.
| Technology | Typical Speeds | Latency | Portability | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5G Cellular (w/ Router) | 50-250+ Mbps / 10-50 Mbps | Low (20-50ms) | Excellent (Works anywhere with a signal) | RVers and remote workers needing a balance of speed and mobility. |
| Starlink (Satellite) | 100-200 Mbps / 10-20 Mbps | Medium (40-100ms) | Good (Requires clear sky view, some plan limits) | Stationary homes with no cell signal but a clear view of the sky. |
| Fixed Wireless (WISP) | 25-100 Mbps / 5-20 Mbps | Low (20-60ms) | None (Tied to one address) | Permanent rural homes with a direct line of sight to a provider's tower. |
| Cellular Booster | Varies (Improves existing signal) | Varies | Fair (Requires existing signal to boost) | Enhancing voice calls and basic data, not a primary internet solution. |
As you can see, a dedicated 5G cellular setup using a router often hits that perfect sweet spot. It delivers speeds that compete with or even beat the others, but with much lower latency than satellite—a critical detail for anything real-time, like Zoom calls or online gaming. For a much deeper dive, check out our 5G home internet reviews.
The biggest advantage of a dedicated 5G cellular solution is its unique blend of high speed, low latency, and true portability. It’s the only option that delivers a fiber-like experience without tying you to a fixed location or suffering from the high latency inherent in satellite technology.
Understanding the Trade-Offs
Let's be real: no single solution is perfect for everyone. Starlink, for example, has been an absolute game-changer for people in the middle of nowhere with zero cell signal. But its higher latency and the absolute need for a wide-open view of the sky can be deal-breakers, especially for RVers who often find themselves parked among the trees.
Fixed Wireless, usually from a local Wireless Internet Service Provider (WISP), can be an incredibly stable and reliable option. The catch? It has zero portability. The service is beamed from a tower directly to a receiver on your house, making it a solution only for a permanent home.
And finally, there are cellular boosters. These are fantastic tools for what they're built to do: make your voice calls clearer and give a little nudge to a weak data signal. But a booster is not a substitute for a dedicated internet system. It can only amplify the signal it receives—if you start with a bad signal, a booster just gives you a stronger bad signal.
A 5G router and antenna system, on the other hand, is engineered from the ground up to pull in and optimize that signal for a fast, reliable data connection. This makes it a far better choice for anyone who actually depends on their internet for work, streaming, or just staying in touch with the world.
Answering Your Rural 5G Questions
After digging into the world of rural 5G coverage, you probably have a few practical questions kicking around. Let's tackle the most common ones head-on so you can finalize your setup and get online with confidence.
Can I Just Use My Phone Hotspot?
It’s the first thing everyone thinks of, but relying on your phone's hotspot for full-time internet is like using a spare tire to drive cross-country. Sure, it works in a pinch, but it’s just not built for the long haul. A phone hotspot is designed for occasional, light use by one or two devices.
A dedicated 5G cellular router, on the other hand, is built from the ground up for constant, heavy-duty performance. It can handle dozens of devices at once—laptops, smart TVs, security cameras, you name it—without overheating or slamming the brakes on your speed.
Most importantly, a real router has ports for external antennas. Those are absolutely essential for pulling in a weak rural signal that a phone could never hope to catch.
This diagram helps visualize which solution makes the most sense depending on your situation.
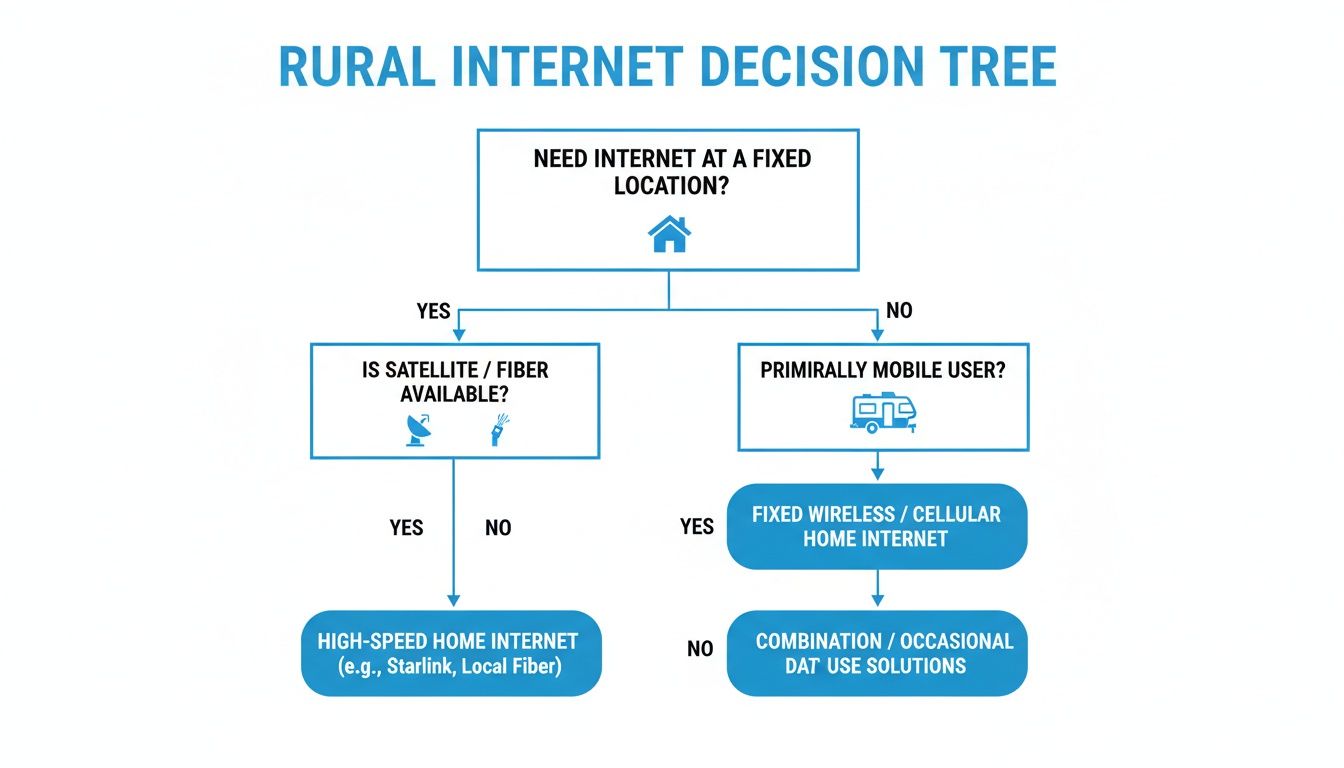
The key takeaway is simple: for consistent, reliable internet at home or in an RV, dedicated hardware is always the way to go.
How Do I Find the Closest Cell Tower?
Finding the right cell tower is the first real step to a great signal. You can't just look up and spot them, but thankfully, there are several fantastic apps and websites that do the detective work for you.
Tools like CellMapper and OpenSignal are indispensable for anyone living out in the sticks. They use crowdsourced data to build detailed maps that show you tower locations, which carriers are on them, and even the specific signal bands they're broadcasting.
Fire up one of these apps on your phone and take a walk around your property or scout a new RV spot. You'll quickly figure out which direction has the strongest signal, which is exactly what you need to know for aiming a directional antenna.
Will a Cell Phone Booster Improve My Internet Speed?
This is probably the biggest point of confusion out there, and the answer is almost always no—at least not in the way you're hoping. A cell phone booster is engineered to do one thing well: improve the quality and reliability of voice calls. It takes a weak signal, amplifies everything (including the noise), and rebroadcasts it over a small indoor area.
A cell phone booster is for better voice calls. A 5G router with an external antenna is for better data. They both work with cellular signals, but they are built for fundamentally different jobs.
While a booster might give your data a tiny lift, it’s not optimized for the high-throughput demands of today's internet. The technology inside a booster can add latency (lag) and just isn't designed to handle the constant, heavy data loads from streaming, video calls, and big downloads.
If you want a fast, stable internet connection, a 5G cellular router hooked up to a high-gain external antenna is a much more effective solution. That combination is purpose-built to maximize data throughput, pulling in the cleanest signal possible and delivering it straight to your devices for the best rural 5G coverage you can get.
Ready to stop struggling with slow, unreliable internet? SwiftNet Wifi specializes in high-speed 5G solutions designed specifically for rural homes and RV travelers. Get the powerful, dependable connection you deserve.
Find Your Perfect Rural 5G Plan Today
#rv #rvlife #rvliving #rvlifestyle #rvrenovation #rvremodel #rvtravel #rvcamping #rvadventures #ruralwifi #5gwifi #5ginternet

















































